Upload Image Using Multer, Express & Mongoose
Pavan Sargar
|

Share Post:
How to upload images using Multer, NodeJs, Express & Mongoose, if you are searching for a perfect tutorial, then you've arrived at the right page. Today in this post we'll learn how to upload an image using Multer, and store it into the MongoDB database, also, display it back to the front-end.
Final Output:
So, without any further ado let's get to the Code!
Setup Code File
Note: Before starting, make sure that you've installed NodeJs & MongoDB locally in your system.
Open a new folder in VS code or any code editor you like, and set up a basic Express Server. You can check out our post on how to create a web server using Node & Express if you don't know how to create one.
Packages we'll use -
Paste below code inside terminal & hit enter to install these NPM packages.
npm i express body-parser multer ejs mongoose
Below code will be our boilerplate.
app.js
const express = require("express");
const bodyParser = require("body-parser");
const multer = require("multer");
const path = require("path");
const fs = require("fs");
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const app = express();
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
app.set("view engine", "ejs");
app.listen(5000, () => {
console.log("Server is listening on Port 5000");
});
Folder Structure -
- MulterImageUpload
- uploads
- views
- index.ejs
- app.js
Our basic code file has been set up, now let's initialize the Multer package.
Let's Initialize Multer
What is Multer?
Before starting out let's first understand what is Multer, it's a NodeJs Middleware, which helps us to upload files on our server. Note Multer only works with multipart/form-data encoding type, which we'll define in HTML form while making a post request.
Just after app.set("view engine", "ejs");, paste below code.
const storage = multer.diskStorage({
destination: function (req, file, cb) {
cb(null, "uploads");
},
filename: function (req, file, cb) {
cb(
null,
file.fieldname + "-" + Date.now() + path.extname(file.originalname)
);
},
});
const upload = multer({ storage: storage });
Here, we are setting up our storage by initializing diskStorage, which gives us complete control over storing files to disk. Inside diskStorage object, we will be defining our destination to store our images, which is an uploads folder.
Now, we will be setting our filename to the image uploaded, in callback, we'll pass Multer's method file.fieldname which will give us the name of the input & bind it with the date. Finally joining it with the original file extension, for eg: png, jgp, etc.
Initialize Mongoose -
mongoose.connect("mongodb://localhost:27017/Multertest", {
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true,
}, (err) => {
if (err) return console.log(err);
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("MongoDB Server listening on 3000");
});
});
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.render("index");
)};
const imageSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
image: {
data: Buffer,
contentType: String
}
});
const ImageModel = mongoose.model("Image", imageSchema);
Here we have created a MongoDB server and new Mongoose Schema, which is imageSchema. Inside the image schema object, we have passed image with data type as Buffer & contentType as String, which is important.
Finally, created a new model of imageSchema.
Let's Upload an Image -
views->index.ejs
<form action="/uploadPhoto" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post">
<input class="choose-file-btn" type="file" name="myImage" />
<input class="upload-btn" type="submit" value="Upload Photo" />
</form>
Inside our form, we are creating a post request on /uploadPhoto. In inputs the type="file" is mandatory field & make sure that you give name attribute to it, here we have myImage, which will also be attached as an image name.
app.js
app.post("/uploadPhoto", upload.single("myImage"), (req, res) => {
const obj = {
img: {
data: fs.readFileSync(
path.join(__dirname + "/uploads/" + req.file.filename)
),
contentType: "image/png",
},
};
const newImage = new ImageModel({
image: obj.img,
});
newImage.save((err) => {
err ? console.log(err) : res.redirect("/");
});
});
In Post request, we will be passing a middleware, upload.single("myImage"), here myImage is the name of the input field that we defined in our index.ejs file & single states that we are passing only one image at a time.
Inside the post request, we'll create an obj object, which will hold the data & contentType of the image. You can learn more about Media Types (MIME Types) Mozilla's official web docs.
Now, we'll pass that object obj.img inside a new ImageModel. Finally we'll save it to our database.
At this point we are able to save image to our database, if you have Robo3T, you will see the image object in image collection.
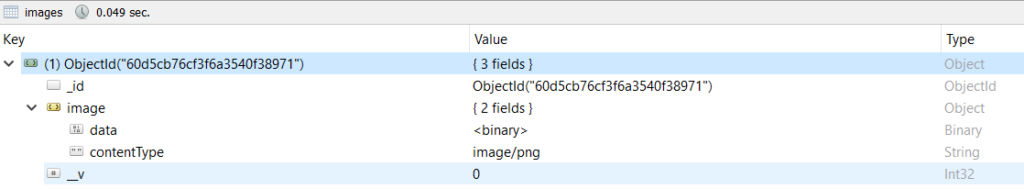
Display the Uploaded Image -
app.js
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
ImageModel.find({}, (err, images) => {
if (err) {
console.log(err);
res.status(500).send("An error occurred", err);
} else {
res.render("index", { images: images });
}
});
});
Inside app.get, let's find the uploaded image, it's nothing fancy simple model.find which is the Mongoose method. Find method gives us access to all images that have been uploaded to the database. We'll get the data that is images, check for error, rendering our index file, and finally, passing the object images from our database.
In your index.ejs file, paste the below code
<div class="uploaded-images">
<% images.forEach(function(image) { %>
<img class="image" src="data:image/<%=image.image.contentType%>;base64,
<%=image.image.data.toString('base64')%>">
<% }); %>
</div>
Now, in our EJS file, we'll render a new img element for every image inside the object by using forEach method. Inside the src attribute, we'll pass the image contentType & will convert its binary data to a string using base64 encoding.
So, we've successfully created an image upload using Multer, Mongoose & NodeJs. Click below to get the complete source code.
I hope this post was helpful, if it was make sure to share it with your friends & also make sure to hit that bell icon in your bottom-left corner to never miss out our new posts.