Fully Functional Contact Form Using Nodemailer
Pavan Sargar
|
Today, we will learn how to send an email in Nodejs by creating a fully functional contact form using Nodemailer. If you have a landing page or a blog, or even any website, having a contact page is important.
There are various ways we could accomplish this task, but we don't want to go into complicated stuff, do we? So, we will be using Nodemailer. We'll learn about Nodemailer a bit later.
This will be our final goal,
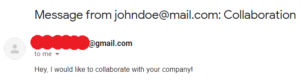
Mail Received!
What is Nodemailer?
Nodemailer is a Nodejs module that lets us send emails in the simplest way. This package can send emails to various email platforms, but today we will be using Gmail as it's fast and less prone to errors.
You can learn more on Nodemailer official documentation.
So, without wasting any more time let's get started!
Note: scroll below for the complete source code link.
Let's setup our Environment
We will be using AJAX to check the status and update it on to the frontend without refresh the browser page.
NPM Packages we'll use -
- Nodemailer
- Express
- dotenv(just for security)
So, you know the drill, go ahead and set up an Express server. We already have an article on how to create a Nodejs server using Express, in case if you don't know.
Folder Structure -
- public
- css
- style.css
- js
- app.js
- contactform.html
- css
- app.js
Backend Setup -
Just the Basic Setup -
require("dotenv").config();
const express = require("express");
const nodemailer = require("nodemailer");
const app = express();
app.use(express.static("public"));
app.use(express.json());
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000;
const user = "your gmail id";
const pass = "your gmail password";
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(__dirname + "/public/contactform.html");
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on port: ${port}...`);
});
Here, we've just done some basic stuff, setting up the server, requiring packages, etc. The important part is that we will be using express.static method to serve our static files from the public folder.
Nodemailer Setup -
app.post("/", (req, res) => {
const transporter = nodemailer.createTransport({
service: "gmail",
auth: {
user,
pass,
},
});
const mailOptions = {
from: req.body.email,
to: "youremail@gmailcom",
subject: `Message from ${req.body.email}: ${req.body.subject}`,
text: req.body.message,
};
transporter.sendMail(mailOptions, (error, responose) => {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
res.send("error");
} else {
console.log("Email Sent");
res.send("success");
}
});
});
On POST request of our root route (or home route), we'll initialize Nodemailer. Inside the transporter object, we'll use the Nodemailer method createTransport, which is an object that holds the service & user authentication details to that particular service. In this case, we are using Gmail.
Note: Make sure your credentials are correct to avoid any further errors.
Now, we'll create an object of email options(mail data), which will be sent using the defined transporter object.
Finally, using the transporter.sendMail method, we'll send the mail using the mailOptions that we defined previously. Now let's handle the error, simple if & else statement. It's important to send a response back to the frontend so that it can update the status.
So, this is it for the Backend part, let's set up the frontend!
Frontend Setup -
<div class="form-container">
<form action="/" class="contact-form">
<h2>Contact Form</h2>
<input type="text" placeholder="Full Name" name="" id="name"><br>
<input type="text" placeholder="Email" name="" id="email"><br>
<input type="text" placeholder="subject" name="" id="subject"><br>
<textarea name="" placeholder="Message" id="message" cols="30" rows="10"></textarea><br>
<input type="submit" id="send-btn" class="submit" value="Send Message">
</form>
</div>
<script src="/js/app.js"></script>
This is the Form, make sure that you have a button or input of type submit to actually submit a form.
let contactForm = document.querySelector(".contact-form");
let name = document.getElementById("name");
let email = document.getElementById("email");
let subject = document.getElementById("subject");
let message = document.getElementById("message");
let send = document.getElementById("send-btn");
Getting hold of the form, and all the inputs.
contactForm.addEventListener("submit", (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
let formData = {
name: name.value,
email: email.value,
subject: subject.value,
message: message.value,
};
send.value = "Sending Message...";
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open("POST", "/");
xhr.setRequestHeader("content-type", "application/json");
xhr.onload = () => {
console.log(xhr.responseText);
if (xhr.responseText == "success") {
name.value = "";
email.value = "";
subject.value = "";
message.value = "";
send.value = "Message Sent Successfully!";
} else {
send.value = "Something Went Wrong!";
}
};
xhr.send(JSON.stringify(formData));
});
Ok, now we'll be adding an event listener "submit" to the form, and hold that event, and use a method preventDefault(). This method will avoid the page refresh on form submit.
Let's create an object to hold the form data that the user has entered. Now, we can change the value of the button to "sending message...".
Let's set up the AJAX, if you've worked with it previously then you know the drill. The important part here is (everything's important) xhr.open method, which takes two parameters,
- Type of Request(POST in this case)
- URL(where this request has to be processed)
xhr.setRequestHeader also takes two parameters,
- Content Type
- Application type (we'll be using JSON ofcourse)
Check out AJAX w3schools docs for more info.
The xhr.onload method, this method only gets executed when the file to be executed is loaded, in this case, it's a submit event.
Here, we'll check if the xhr.responseText (gives the server response as a text) is equal to "success" (which we sent from the server at successful mail). If it's a success then we'll change the send.value = "Message Sent Successfully" and will empty out all the input fields.
Finally, we'll send the data from the frontend to our server in string format, as we can't send it in JSON format. Make sure that xhr.send(JSON.stringify(formData)); the method is defined outside the xhr.onload method.
Google Account Setting to Avoid Errors
Ok, now we've finished with our frontend and backend, but before that let's check if your Gmail gives an error and solve it. If you get any error saying verification fail or something, follow the below steps to solve it.
- Disable 2 Factor Authentication
- If you've enabled 2FA on your Google Account, you'll not be able to send mail through Nodemailer.
- Enable Less Secure App Access
- To enable this setting you need to disable the 2FA
I hope this post was helpful, if it was make sure to share it with your friends!
